1. 概述
LaunchAnyWhere漏洞比较早的分析可以参考retme的文章,后来Google给这种漏洞命名为Intent Redirection。LaunchAnyWhere顾名思义就是能够调用任意未导出的Activity。
2. 漏洞成因
2.1. Google Bug 7699048
AccountManagerService是系统服务之一,暴露给开发者的的接口是AccountManager。该服务用于管理用户各种网络账号。这使得一些应用可以获取用户网络账号的token,并且使用token调用一些网络服务。这种设计的本意是,AccountManagerService帮助AppA查找到AppB账号登陆页面,并呼起这个登陆页面。而问题在于,AppB可以任意指定这个intent所指向的组件,AppA将在不知情的情况下由AccountManagerResponse调用起了一个Activity。如果AppA是一个system权限应用,比如Settings,那么AppA能够调用起任意AppB指定的未导出Activity。
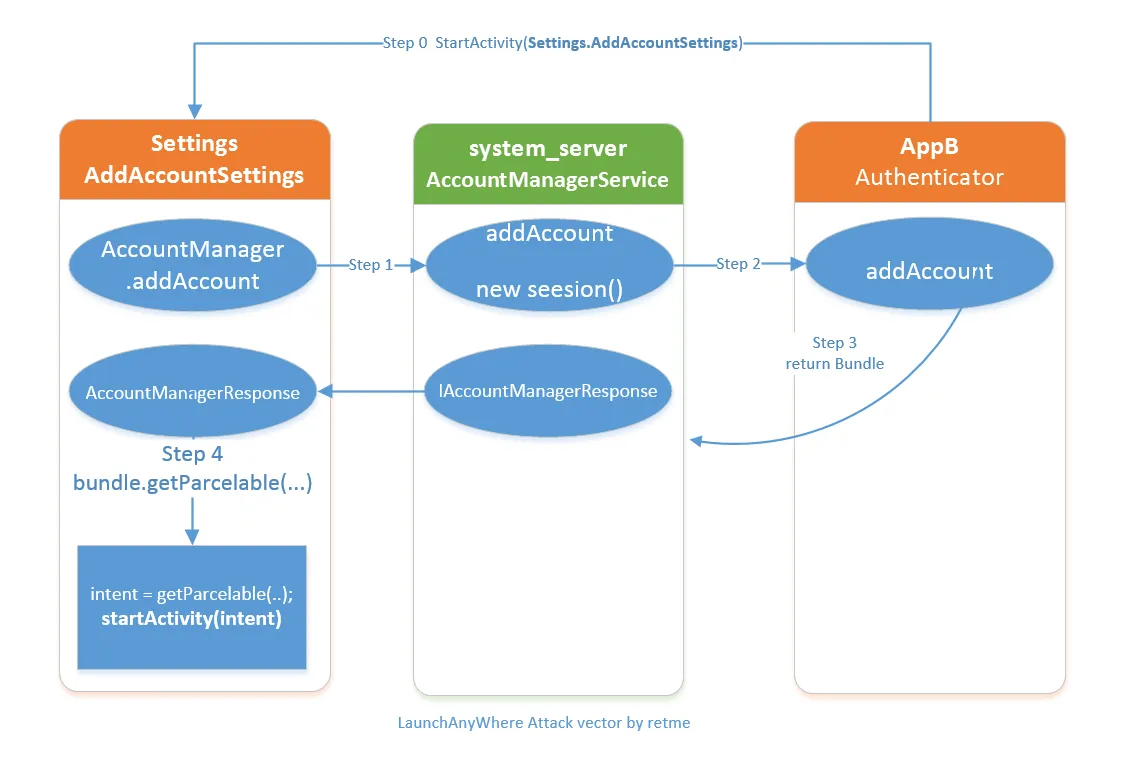
此漏洞比较经典的流程图,当AppA是Settings,可以简单理解成以下流程:
AppB调用com.android.settings.accounts.AddAccountSettings,使Settings请求添加一个特定类型的网络账号- 系统查询到
AppB可以提供一个该类型的网络账号服务,系统向AppB发起请求 AppB返回了一个intent给系统,系统把intent转发给SettingsAccountManagerResponse在Settings的进程空间内调用startActivity(intent)调起一个Activity,AccountManagerResponse是FrameWork中的代码,AppA对这一调用毫不知情。
最终关键触发点在此处
/** Handles the responses from the AccountManager */
private class Response extends IAccountManagerResponse.Stub {
public void onResult(Bundle bundle) {
Intent intent = bundle.getParcelable(KEY_INTENT);
if (intent != null && mActivity != null) {
// since the user provided an Activity we will silently start intents
// that we see
mActivity.startActivity(intent);
// leave the Future running to wait for the real response to this request
} else if (bundle.getBoolean("retry")) {安卓4.4已经修复了这个漏洞,检查了Step3中返回的intent所指向的Activity和AppB是否是有相同签名的。避免了LaunchAnyWhere的可能。
+ @Override
public void onResult(Bundle result) {
mNumResults++;
- if (result != null && !TextUtils.isEmpty(result.getString(AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN))) {
+ Intent intent = null;
+ if (result != null
+ && (intent = result.getParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT)) != null) {
+ /*
+ * The Authenticator API allows third party authenticators to
+ * supply arbitrary intents to other apps that they can run,
+ * this can be very bad when those apps are in the system like
+ * the System Settings.
+ */
+ PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager();
+ ResolveInfo resolveInfo = pm.resolveActivity(intent, 0);
+ int targetUid = resolveInfo.activityInfo.applicationInfo.uid;
+ int authenticatorUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
+ if (PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH !=
+ pm.checkSignatures(authenticatorUid, targetUid)) {
+ throw new SecurityException(
+ "Activity to be started with KEY_INTENT must " +
+ "share Authenticator's signatures");
+ }
+ }
+ if (result != null
+ && !TextUtils.isEmpty(result.getString(AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN))) {2.2. Google Bug 17356824
和Google Bug 7699048是同一个流程,但不同的是漏洞成因不同,这次是Settings调用了AccountManager.addAccount。在传递的AddAccountOptions参数时加入了一个PendingIntent,其intent类型是Broadcast。注意这个PendingIntent是Settings创建的,拥有system权限。
private void addAccount(String accountType) {
Bundle addAccountOptions = new Bundle();
mPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, new Intent(), 0);
addAccountOptions.putParcelable(KEY_CALLER_IDENTITY, mPendingIntent);
addAccountOptions.putBoolean(EXTRA_HAS_MULTIPLE_USERS, Utils.hasMultipleUsers(this));
AccountManager.get(this).addAccount(因为Settings初始化PendingIntent的时候传入的是一个没有内容的new Intent(),所以攻击者在调用PendingIntent.send()的时候可以随意设置Intent中的大部分内容。这是由于在系统源码中PendingIntentRecord.sendInner调用了finalIntent.fillIn(intent, key.flags),允许调用者填充Intent的值。
int sendInner(int code, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IIntentReceiver finishedReceiver, String requiredPermission,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int flagsMask, int flagsValues, Bundle options) {
synchronized(owner) {
if (!canceled) {
sent = true;
if ((key.flags&PendingIntent.FLAG_ONE_SHOT) != 0) {
owner.cancelIntentSenderLocked(this, true);
canceled = true;
}
Intent finalIntent = key.requestIntent != null
? new Intent(key.requestIntent) : new Intent();
if (intent != null) {
int changes = finalIntent.fillIn(intent, key.flags);因此只要AppB在step3的时候取到了AddAccountOptions参数,从中获得了这个PendingIntent,并且可以利用它以system的身份发送广播,示例代码如下:
PendingIntent pending_intent = (PendingIntent)options.get("pendingIntent");
intent.setAction("android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED");
try {
pending_intent.send(getGlobalApplicationContext(),0,intent,null,null,null);
} catch (CanceledException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}在此补丁中填充了无意义的值,防止攻击者重新填充Intent
private void addAccount(String accountType) {
Bundle addAccountOptions = new Bundle();
- mPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, new Intent(), 0);
+ /*
+ * The identityIntent is for the purposes of establishing the identity
+ * of the caller and isn't intended for launching activities, services
+ * or broadcasts.
+ *
+ * Unfortunately for legacy reasons we still need to support this. But
+ * we can cripple the intent so that 3rd party authenticators can't
+ * fill in addressing information and launch arbitrary actions.
+ */
+ Intent identityIntent = new Intent();
+ identityIntent.setComponent(new ComponentName(SHOULD_NOT_RESOLVE, SHOULD_NOT_RESOLVE));
+ identityIntent.setAction(SHOULD_NOT_RESOLVE);
+ identityIntent.addCategory(SHOULD_NOT_RESOLVE);
+
+ mPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, 0, identityIntent, 0);
addAccountOptions.putParcelable(KEY_CALLER_IDENTITY, mPendingIntent);
addAccountOptions.putBoolean(EXTRA_HAS_MULTIPLE_USERS, Utils.hasMultipleUsers(this));
AccountManager.get(this).addAccount(2.3. CVE-2020-0144
SliceProvider是自Android P开始引入的一种应用程序间共享UI界面的机制,可以通过SettingsSliceProvider中的ContentProvider来共享给别的应用使用,用户不必打开Settings,就可以在其他应用界面中对某些设置进行操作。
关键漏洞位置在frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/keyguard/KeyguardSliceProvider.java生成了一个无Package和Action的PendingIntent,具体代码如下
public boolean onCreateSliceProvider() {
...
mPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(getContext(), 0, new Intent(), 0);
...
}
return true;
}接下来通过父类SliceProvider的call方法返回包含该Intent的Bundle,具体代码如下:
@Override
public Bundle call(String method, String arg, Bundle extras) {
if (method.equals(METHOD_SLICE)) {
Uri uri = getUriWithoutUserId(validateIncomingUriOrNull(
extras.getParcelable(EXTRA_BIND_URI)));
List<SliceSpec> supportedSpecs = extras.getParcelableArrayList(EXTRA_SUPPORTED_SPECS);
String callingPackage = getCallingPackage();
int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
Slice s = handleBindSlice(uri, supportedSpecs, callingPackage, callingUid, callingPid);
Bundle b = new Bundle();
b.putParcelable(EXTRA_SLICE, s);
return b;
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_MAP_INTENT)) {
...
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_MAP_ONLY_INTENT)) {
...
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PIN)) {
...
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_UNPIN)) {
...
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_GET_DESCENDANTS)) {
...
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_GET_PERMISSIONS)) {
...
}
return super.call(method, arg, extras);
}难点在于如何拿到这个PendingIntent,具体思路可以参考文章Android 中的特殊攻击面(三)—— 隐蔽的 call 函数。
该漏洞补丁相当于指定了Package,细节如下:
mZenModeController = new ZenModeControllerImpl(getContext(), mHandler);
mZenModeController.addCallback(this);
mDatePattern = getContext().getString(R.string.system_ui_aod_date_pattern);
- mPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(getContext(), 0, new Intent(), 0);
+ mPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(getContext(), 0,
+ new Intent(getContext(), KeyguardSliceProvider.class), 0);
mMediaWakeLock = new SettableWakeLock(WakeLock.createPartial(getContext(), "media"),
"media");
KeyguardSliceProvider.sInstance = this;同样也有公开POC可以参考。
2.4. CVE-2021-39707
最终漏洞触发位置在com/android/settings/users/AppRestrictionsFragment.java,相关代码为:
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
Bundle results = getResultExtras(true);
final ArrayList<RestrictionEntry> restrictions = results.getParcelableArrayList(
Intent.EXTRA_RESTRICTIONS_LIST);
Intent restrictionsIntent = results.getParcelable(CUSTOM_RESTRICTIONS_INTENT);
if (restrictions != null && restrictionsIntent == null) {
onRestrictionsReceived(preference, restrictions);
if (mRestrictedProfile) {
mUserManager.setApplicationRestrictions(packageName,
RestrictionsManager.convertRestrictionsToBundle(restrictions), mUser);
}
} else if (restrictionsIntent != null) {
preference.setRestrictions(restrictions);
if (invokeIfCustom && AppRestrictionsFragment.this.isResumed()) {
assertSafeToStartCustomActivity(restrictionsIntent);
int requestCode = generateCustomActivityRequestCode(
RestrictionsResultReceiver.this.preference);
AppRestrictionsFragment.this.startActivityForResult(
restrictionsIntent, requestCode);
}
}
}此漏洞是assertSafeToStartCustomActivity校验不足产生的,相关代码:
private void assertSafeToStartCustomActivity(Intent intent) {
// Activity can be started if it belongs to the same app
if (intent.getPackage() != null && intent.getPackage().equals(packageName)) {
return;
}
// Activity can be started if intent resolves to multiple activities
List<ResolveInfo> resolveInfos = AppRestrictionsFragment.this.mPackageManager
.queryIntentActivities(intent, 0 /* no flags */);
if (resolveInfos.size() != 1) {
return;
}
// Prevent potential privilege escalation
ActivityInfo activityInfo = resolveInfos.get(0).activityInfo;
if (!packageName.equals(activityInfo.packageName)) {
throw new SecurityException("Application " + packageName
+ " is not allowed to start activity " + intent);
}
}其中,正常情况下resolveInfos.size() != 1可筛选出Intent为多个目标的情况,触发用户选择的流程从而防止漏洞触发。但是Activity在Manifest中有一个配置叫做android:priority,如果其中存在高优先级的Activity则会被直接选择,并不会触发用户选择的流程。但刚好PrivilegedCallActivity符合利用场景,相关漏洞利用参考CVE的别样发现之旅 | AOSP Bug Hunting with appshark。
最终官方给出的补丁代码如下:
if (intent.getPackage() != null && intent.getPackage().equals(packageName)) {
return;
}
- // Activity can be started if intent resolves to multiple activities
- List<ResolveInfo> resolveInfos = AppRestrictionsFragment.this.mPackageManager
- .queryIntentActivities(intent, 0 /* no flags */);
- if (resolveInfos.size() != 1) {
- return;
+ ResolveInfo resolveInfo = mPackageManager.resolveActivity(
+ intent, PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY);
+
+ if (resolveInfo == null) {
+ throw new ActivityNotFoundException("No result for resolving " + intent);
}
// Prevent potential privilege escalation
- ActivityInfo activityInfo = resolveInfos.get(0).activityInfo;
+ ActivityInfo activityInfo = resolveInfo.activityInfo;
if (!packageName.equals(activityInfo.packageName)) {
throw new SecurityException("Application " + packageName
+ " is not allowed to start activity " + intent);2.5. CVE-2022-20223
漏洞利用流程和CVE-2021-39707类似,只不过是校验函数的二次绕过。
由于intent.getPackage()和getPackageManager().resolveActivity(intent, PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY).activityInfo.packageName获得packageName逻辑不一致,导致校验不足。其中intent.getPackage()是针对private String mPackage;,而resolve方式是如果存在private ComponentName mComponent;则取该值,否则取mPackage。
对应的修复补丁也比较简单,代码如下:
private void assertSafeToStartCustomActivity(Intent intent) {
- // Activity can be started if it belongs to the same app
- if (intent.getPackage() != null && intent.getPackage().equals(packageName)) {
- return;
- }
+ EventLog.writeEvent(0x534e4554, "223578534", -1 /* UID */, "");
ResolveInfo resolveInfo = mPackageManager.resolveActivity(
intent, PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY);3. 漏洞利用
3.1. launch a component
调用startActivity, startActivityForResult, startService, sendBroadcast时使用不可信的intent,可能导致唤起私有的Activity
3.2. return data
调用setResult时使用不可信的intent,可能导致app隐私数据泄露
